what can humans do to solve the issue of scarcity?
Definition: Scarcity refers to resources being finite and express. Scarcity ways nosotros accept to determine how and what to produce from these limited resources. It means there is a constant opportunity cost involved in making economic decisions. Scarcity is i of the primal issues in economics.
Examples of scarcity
- Land – a shortage of fertile land for populations to grow food. For example, the desertification of the Sahara is causing a decline in land useful for farming in Sub-Saharan African countries.
- H2o scarcity – Global warming and changing conditions, has caused some parts of the world to become drier and rivers to dry up. This has led to a shortage of drinking water for both humans and animals.
- Labour shortages. In the mail service-war period, the U.k. experienced labour shortages – bereft workers to fill jobs, such every bit bus drivers. In more recent years, shortages have been focused on particular skilled areas, such as nursing, doctors and engineers
- Health care shortages. In whatever wellness care system, there are limits on the available supply of doctors and hospital beds. This causes waiting lists for certain operations.
- Seasonal shortages. If in that location is a surge in demand for a popular Christmas nowadays, it can crusade temporary shortages as need as greater than supply and it takes time to provide.
- Fixed supply of roads. Many city centres experience congestion – there is a shortage of road space compared to number of road users. There is a scarcity of available land to build new roads or railways.
How does the free market solve the problem of scarcity?
If nosotros take a good like oil. The reserves of oil are limited; there is a scarcity of the raw material. Every bit we use upward oil reserves, the supply of oil will start to fall.
Diagram of fall in supply of oil
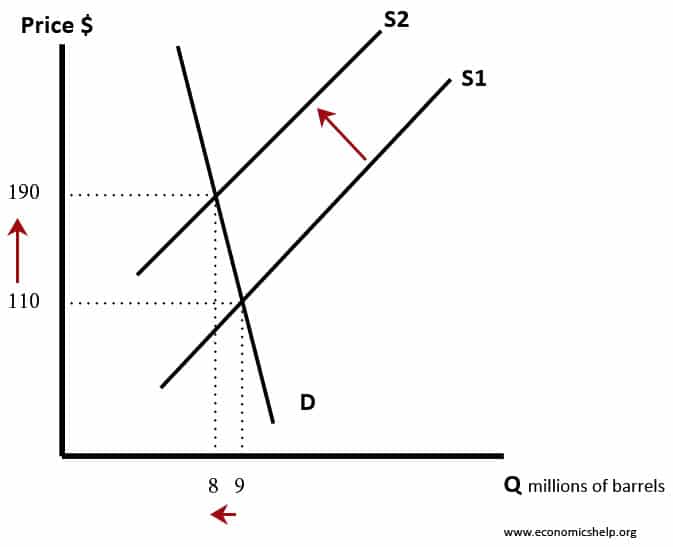
If there is a scarcity of a good the supply will exist falling, and this causes the price to rise. In a costless market, this rising price acts as a signal and therefore demand for the skillful falls (movement along the demand curve). As well, the higher price of the skillful provides incentives for firms to:
- Look for alternative sources of the practiced e.g. new supplies of oil from the Antarctic.
- Look for alternatives to oil, east.1000. solar console cars.
- If we were unable to find alternatives to oil, then we would take to respond by using less send. People would cutting back on transatlantic flights and make fewer trips.
Demand over fourth dimension
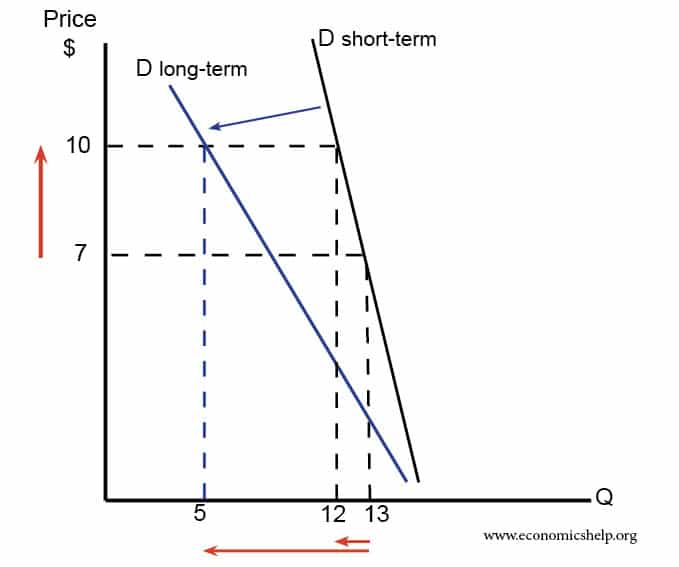
In the short-term, need is toll inelastic. People with petrol cars, need to keep buying petrol. Notwithstanding, over time, people may purchase electric cars or bicycles, therefore, the demand for petrol falls. Demand is more price elastic over time.
Therefore, in a free market place, there are incentives for the market mechanisms to deal with the issue of scarcity.
Causes of scarcity
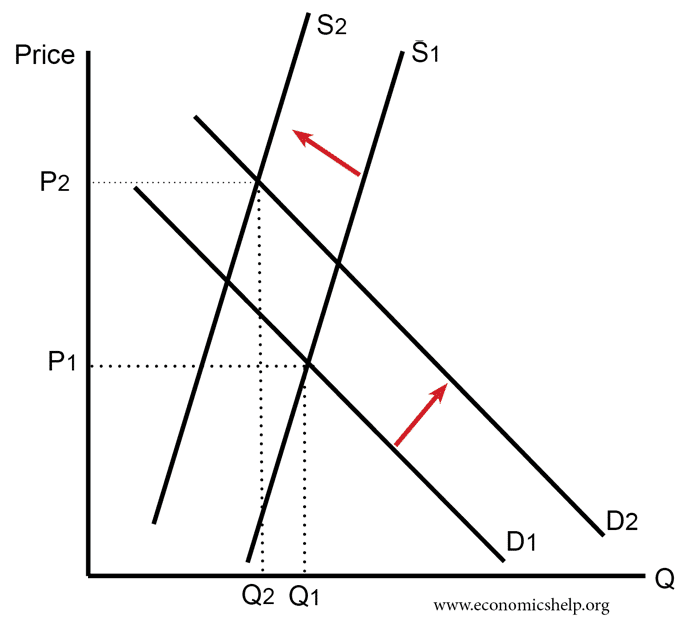
Scarcity can be due to both
- Demand-induced scarcity
- Supply-induced scarcity
and a combination of the 2. Run into more than at: Causes of scarcity.
Scarcity and potential marketplace failure
With scarcity, there is a potential for market failure. For instance, firms may non recall nigh the time to come until it is likewise late. Therefore, when the good becomes scarce, there might not be any practical culling that has been adult.
Some other trouble with the free marketplace is that since goods are rationed by toll, there may be a danger that some people cannot afford to buy certain goods; they take limited income. Therefore, economic science is as well concerned with the redistribution of income to help everyone be able to afford necessities.
Another potential market failure is a scarcity of environmental resource. Decisions we take in this present generation may touch the future availability of resources for futurity generations. For case, the production of CO2 emissions atomic number 82 to global warming, rising body of water levels, and therefore, future generations will confront less available land and a shortage of drinking water.
The problem is that the free market is not factoring in this impact on future resources availability. Product of CO2 has negative externalities, which worsen future scarcity.
Tragedy of the commons
The tragedy of the commons occurs when there is over-grazing of a item land/field. It tin can occur in areas such as abyssal fishing which crusade loss of fish stocks. Once again the free-market may fail to adequately deal with this deficient resource.
Further reading on Tragedy of the Eatables
Quotas and scarcity
Ane solution to dealing with scarcity is to implement quotas on how much people tin can purchase. An example of this is the rationing organisation that occurred in the 2d World War. Because there was a scarcity of food, the government had strict limits on how much people could get. This was to ensure that even people with low incomes had access to food – a bones necessity.
A trouble of quotas is that it can lead to a black market; for some goods, people are willing to pay high amounts to get extra food. Therefore, it can exist difficult to police a rationing system. But, it was a necessary policy for the second earth war.
Related pages
- Opportunity price
- Product possibility frontiers
- Is economics irrelevant in the absence of scarcity?
- Dealing with food scarcity
Source: https://www.economicshelp.org/blog/586/markets/scarcity-in-economics/
0 Response to "what can humans do to solve the issue of scarcity?"
إرسال تعليق